Understanding Basic Life Support: A Comprehensive Guide
What is Basic Life Support?
Basic Life Support (BLS) refers to the type of care that first responders, healthcare providers, and public safety professionals provide to anyone experiencing cardiac arrest, respiratory distress, or an obstructed airway. BLS is a fundamental skill that can save lives by maintaining airways, supporting breathing, and ensuring adequate circulation until advanced medical help arrives.
The Importance of Learning BLS
Learning BLS is crucial not only for healthcare professionals but also for the general public. In emergency situations where every second counts, having the ability to perform BLS can mean the difference between life and death. Bystanders trained in BLS can provide immediate assistance, improving the chances of survival and recovery for the person in distress.
Key Components of BLS
BLS involves several critical components, each designed to manage life-threatening situations effectively:
- Chest Compressions: These help maintain blood circulation in a person whose heart has stopped.
- Airway Management: Ensuring the airway is clear to allow for adequate airflow.
- Rescue Breaths: Providing breaths to ensure oxygen reaches the lungs.
BLS Certification and Training
Obtaining a BLS certification is highly recommended for individuals in many professions, including healthcare, firefighting, and law enforcement. Many organizations offer BLS training courses that cover essential skills such as cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), the use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs), and how to assist choking individuals.
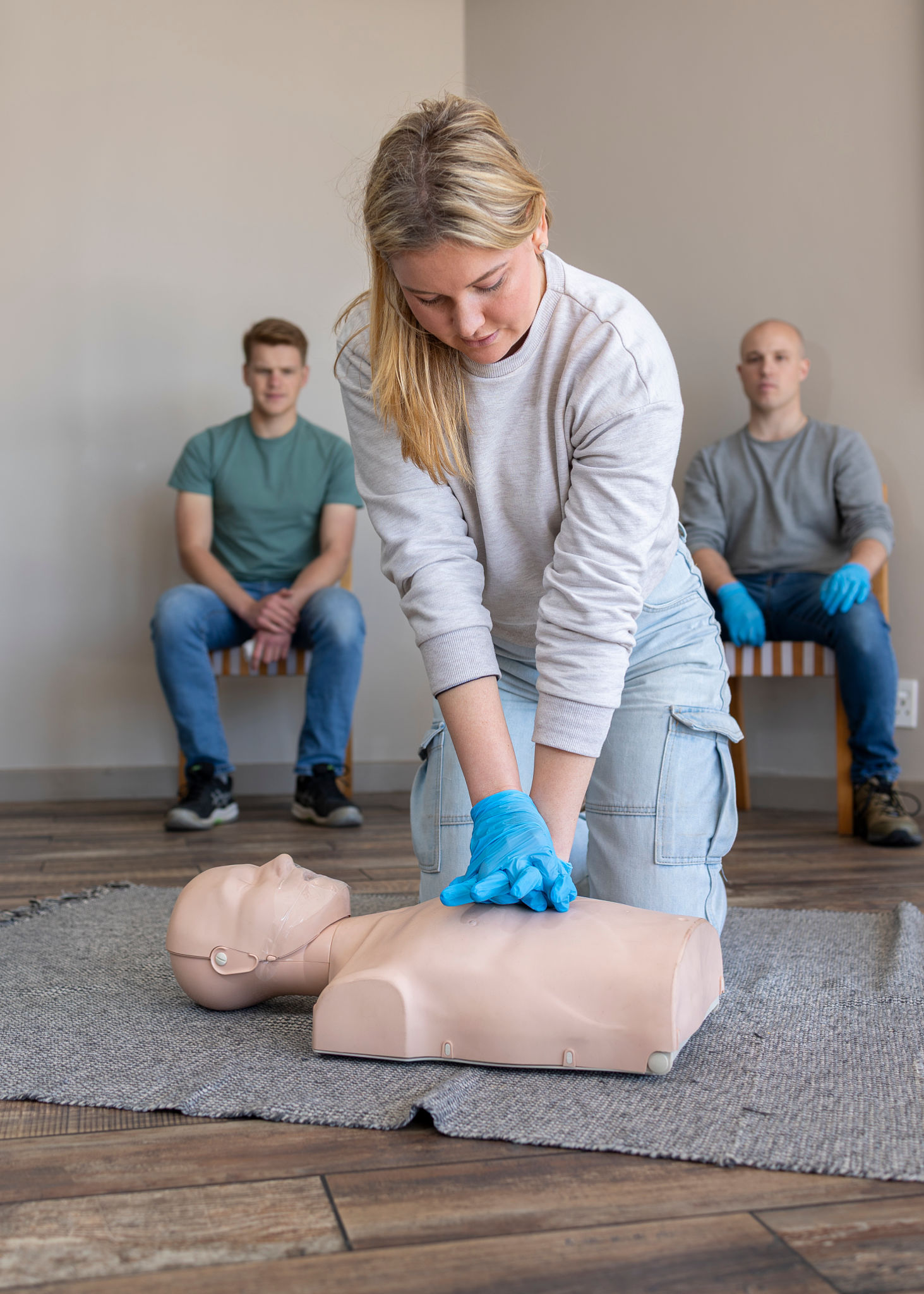

Steps in Performing BLS
When performing BLS, it is important to follow these steps systematically:
- Assess the Situation: Ensure the scene is safe for both the rescuer and the victim.
- Check Responsiveness: Tap and shout to see if the victim responds.
- Call for Help: Dial emergency services or instruct someone else to do so.
- Begin Chest Compressions: Place your hands in the center of the victim's chest and push hard and fast.
- Provide Rescue Breaths: If trained, give two breaths after every 30 compressions.
- Use an AED: Follow the device instructions as soon as it becomes available.
Common Misconceptions About BLS
Several misconceptions surround BLS, which can deter people from taking action in emergencies. One common myth is that performing CPR can cause harm; however, doing something is often better than doing nothing, as time is critical during cardiac arrest. Another misconception is that only professionals can perform BLS, but anyone trained in these techniques can effectively provide aid.

The Role of Technology in BLS
The introduction of technology, such as AEDs, has significantly enhanced the effectiveness of BLS. AEDs are designed to be user-friendly, with voice prompts and visual aids that guide users through the defibrillation process. These devices are increasingly available in public spaces, making it easier for bystanders to provide life-saving interventions quickly.
The Future of BLS Training
The future of BLS training looks promising with advancements in technology and simulation-based learning. Virtual reality and augmented reality are being integrated into training programs to provide realistic scenarios that enhance learning outcomes. These innovative approaches are expected to make BLS training more accessible and engaging, encouraging more people to become certified.
In conclusion, understanding and being able to perform Basic Life Support is a vital skill that can save lives. Whether you're a healthcare provider or a concerned citizen, investing time in learning BLS can equip you with the knowledge and confidence needed to act decisively in emergencies.